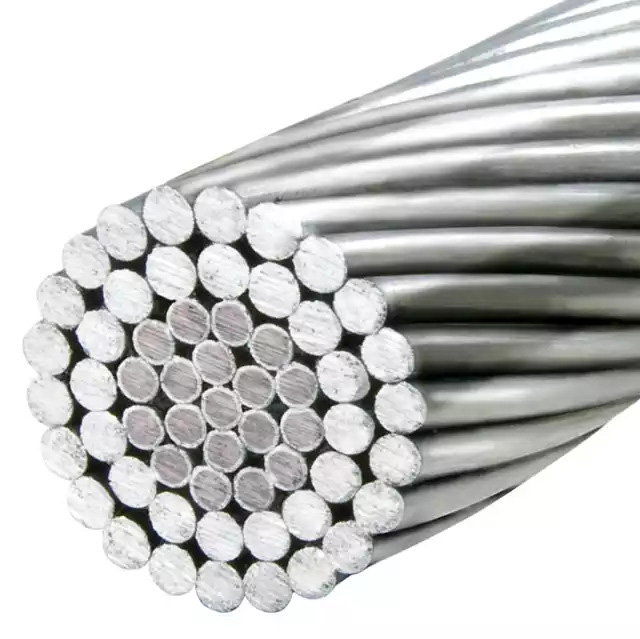
A bare conductor is a cable without an insulation layer. It is suitable for overhead transmission and distribution applications, and does not require any special insulation. Bare conductors are easy to bend and are suitable for most power applications. This article will provide an overview of bare conductors and some of their benefits. This article will also discuss the different types of bare conductors, including round single wires, bare stranded wires, and profiled wires.

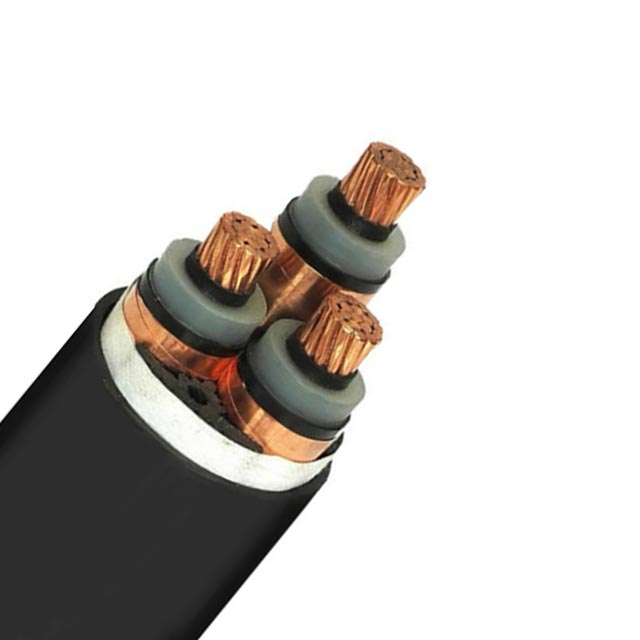
Non-metallic covering on a cable
The new definition for “Jacket” recognises a non-metallic covering on ‘cables’, which is the outer covering of cables like single conductor RA90 and TECK90. This type of cable is designed to provide both mechanical and environmental protection, and is often used for electrical wiring exposed to the elements. The new definition is a step toward making these types of cables safer than older wiring types.
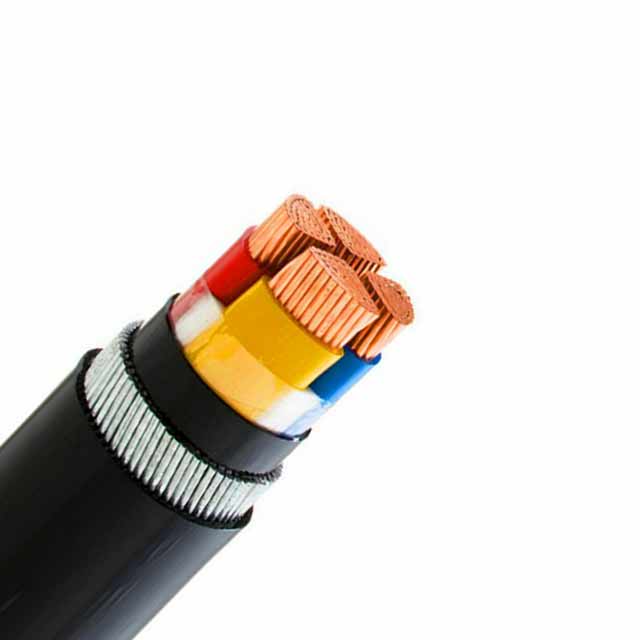
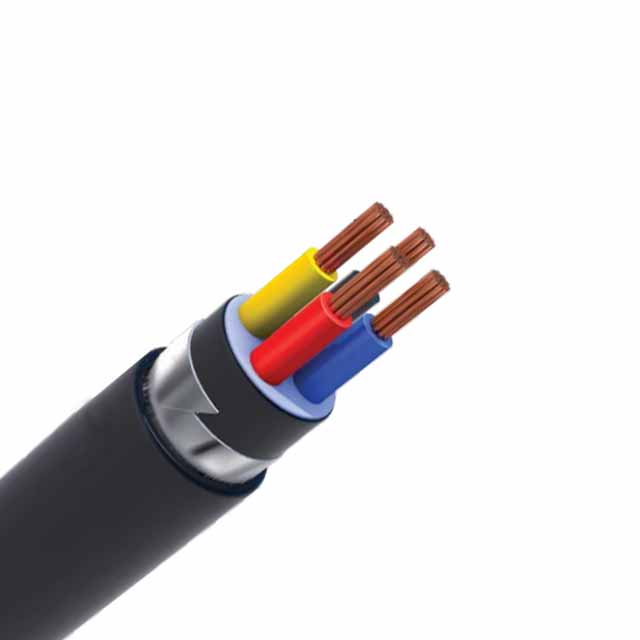
Non-metallic-sheathed cables, or NM-B and NM-C cables, contain individual wires. The NM-B cable is rated to work in a wide temperature range and is suitable for wall-cavity installations. The gauge of the individual wires determines the maximum current the cable can safely handle, and this information should be available on the cable tag.
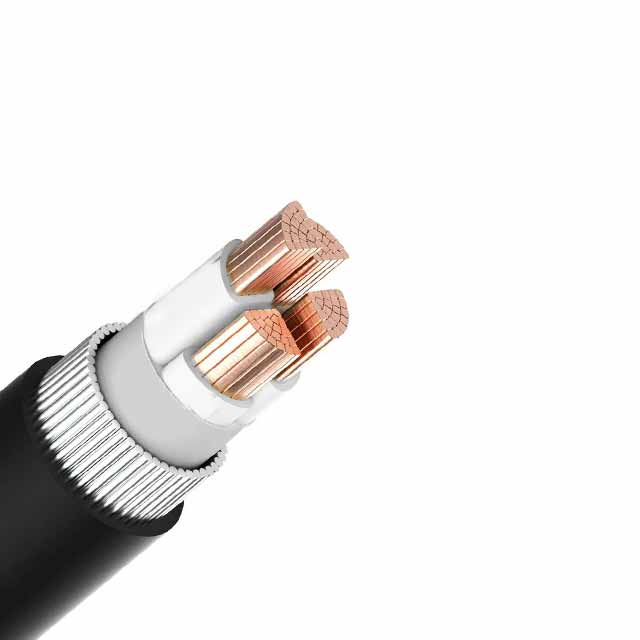
MC, or metal-clad, cable is the most common type of electrical cable and has metal sheathing. The outer covering protects the individual wire conductors from damage, but it does not protect the cable from electromagnetic fields. MC cables are typically bundled in a parallel bundle, so they must be very tight for the circuit to work properly. The MC cable sheathing can be severed using a cable ripper, a metal tool that allows easy connection to a device.
Non-metallic-sheathed cables are used in many applications, including home wiring. These cables come in different colour ranges. NM-B cables are generally black insulated THHN wires, and Type UF is made of aluminum. UF-B cables are resistant to fungi, moisture, and corrosion. Non-metallic-sheathed cables are generally used in residential installations, but are not designed for outdoor installation.
Suitable for overhead transmission and distribution applications
The Bare Conductor is a type of electrical wire used for overhead power transmission and distribution applications. There are many different types of conductor, each with different strengths and span lengths. For example, an All-Aluminum Conductor (AAC) is comprised of one or more bundles of aluminum wire. These are primarily used in coastal areas. In contrast, a Copper Conductor (CC) is used for overhead power transmission and distribution applications.
Covered conductors are not as flexible as bare ones. Their diameters are typically larger and their strength rating is lower. For instance, a 477 kcmil aluminum conductor covered with an 80-mil XLPE conductor covering weighs 20% more than a bare conductor. It also has a lower strength rating and is susceptible to damage. Moreover, they are susceptible to degradation caused by UV radiation and tracking.
Aluminum conductors are also used in overhead power distribution systems. Aluminum conductors have 60% the conductivity of copper, yet are half the weight. However, the tensile strength of aluminum conductors is considerably lower than that of copper. Aluminum conductors are generally more lightweight than copper, which makes them an excellent choice for high-power transmission lines. A good example of a low-voltage overhead transmission system is the bare conductor used for street lighting.
Electric power is commonly transmitted over the air in overhead lines at 765,000 volts between conductors. This voltage is usually more than enough to power a light bulb. In addition, a Bare Conductor is highly recyclable, which means it is more environmentally friendly. Whether you are looking for an overhead power transmission or distribution line, TransPowr(r) Bare Conductor is the right choice.
ACSR conductors are available with a variety of properties and applications. They are ideal for distribution and transmission lines and can be laid in canyons and rivers. ACSR core wires are available with Class A, B, or C galvanizing. ZMS overhead power cable company offers utility-approved wires in Kenya, Rwanda, and Bangladesh. These wires are available in a variety of voltages and lengths.
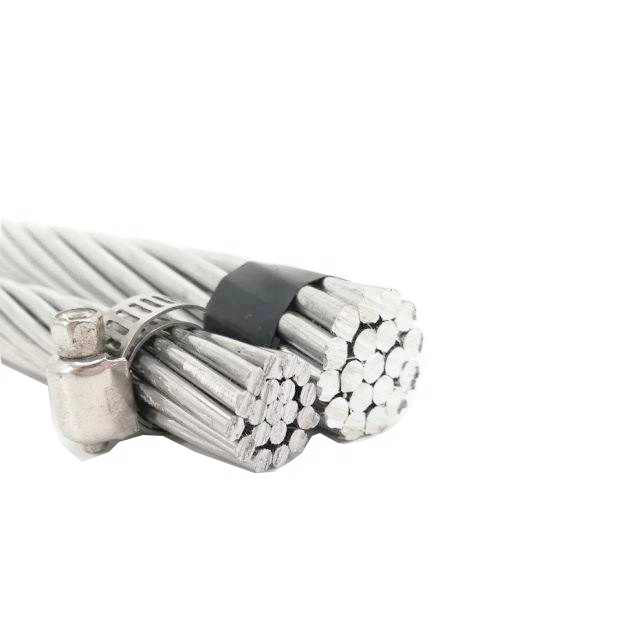

Has no insulation layer
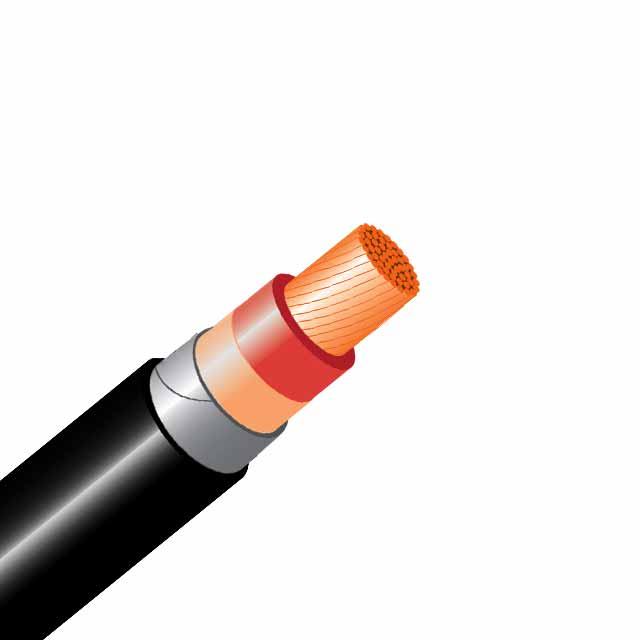
A bare conductor is a wire with no insulation layer. It is the most common type of conductor. This type is often flexible, flat, round, or coaxial with a copper nucleus. In addition, it may be braided or insulated. Bare conductors can be spooling or coiling, or they may be placed in a duct. A semi-rigid cable has a flexible inner core surrounded by an inflexible sheathing material.
The NEC designation for a bare conductor is 600-volts. It may be armored or have a sheath made of thermoplastic material. Other common types are SDN (small diameter multi-conductor control cable) and SE (above-ground service entrance cable).
The parameters for test coils are summarized in Table I. The test coils are made of three components: a DC power source, a cryogenic environment, and a switch. For a bare coil, the equivalent circuit model includes three components: the HTS winding’s self-inductance, the shunt resistor, and the substrate resistance. These parameters are the most commonly measured values.
Easy to bend
There are many benefits to using a bare copper conductor. It’s flexible and comes in a variety of stranding configurations. One common configuration is rope stranding, which allows for maximum flexibility. Southwire is one source of bare copper conductor. This material is also available in a variety of other configurations. Below are some reasons why you should use a bare copper conductor.
The two main types of bare copper wire are hard drawn and soft drawn. Hard drawn copper wire is stiffer and more difficult to bend. Soft drawn copper wire is softer and more flexible, but both types are approved by mil-spec AA59551. Stranded bare copper is less difficult to bend because it is made from multiple thinner strands. This makes it easier to work with than solid drawn bare copper.